Polypropylene (PP) is a colorless, translucent, non-toxic thermoplastic resin. Compared to other general-purpose thermoplastics, it features a low relative density, low cost, and overall excellent performance, making it widely used in various industries such as chemicals, construction, home appliances, agriculture, and transportation.
Based on the spatial arrangement and sequence of methyl group substitutions, polypropylene can be categorized into isotactic, syndiotactic, and atactic polypropylene. The majority of homopolypropylene produced in industrial processes is predominantly isotactic. This article mainly introduces the principle of low-field NMR measurement of polypropylene isotacticity.
Isotactic and syndiotactic polypropylene are stereoregular polymers, and the percentage of stereoregular polymers is referred to as isotacticity.

By measuring isotacticity, we can understand the degree of spatial order of polypropylene molecules and the crystallization properties of the product. The higher the isotacticity, the higher the degree of order, crystallinity, and mechanical properties such as hardness, stiffness, modulus, tensile strength, and yield strength. Additionally, the melting point, thermal stability, aging resistance, and radiation resistance are improved, while toughness, impact resistance, and elongation at break tend to decrease.

NuMag PQ001 Series Low-Field NMR Analyzer
Currently, common analysis methods for testing polypropylene isotacticity include: organic solvent extraction and weighing methods, as well as low-field NMR methods.
The organic solvent extraction method requires a long extraction time, typically around 24 hours, and the solvents used are toxic and harmful. Additionally, the method is influenced by several factors such as the size of polypropylene particles, sample dryness, sample quantity, solvent amount, extraction times, extraction duration, temperature, cooling time, and drying time after extraction, all of which can affect the accuracy of the results.
The low-field NMR method offers advantages such as fast analysis speed, high accuracy, no pollution, and low cost, making it suitable for both research and industrial quality control.
The principle of low-field NMR measurement of polypropylene isotacticity involves exciting the sample with a radiofrequency pulse, causing the atomic nuclei at low energy levels to transition to higher energy levels. When the external radiofrequency pulse is turned off, the high-energy nuclei return to the lower energy state, generating a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal. The observed NMR signal decays exponentially over time, a process known as relaxation. This decay signal provides two types of information: first, the intensity of the NMR signal depends on the number of nuclei being measured in the sample, and second, the speed of the signal decay is related to the movement of the nuclei being measured. Isotactic and syndiotactic polypropylene nuclei decay quickly, while nuclei in atactic polypropylene decay much more slowly.
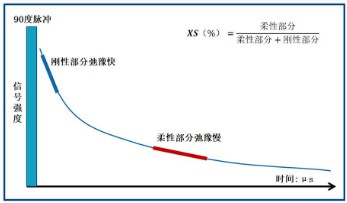
Based on these two characteristics of nuclear magnetic signals, different excitations and samplings of polypropylene allow the corresponding data to be obtained. By further utilizing the relationship between the resonance decay signals of isotactic and syndiotactic polypropylene and the n-heptane extraction values, a linear standard curve is established, enabling accurate determination of polypropylene isotacticity.

Phone: 400-060-3233
After-sales: 400-060-3233


Back to Top