NUMAI low-field NMR equipment offers powerful capabilities across petroleum, rock, geotechnical, and concrete research. For studies involving core, cuttings, permafrost, and concrete, it can perform one-dimensional analyses of conventional porosity, permeability, and fluid (oil/water) saturation, as well as two-dimensional oil, gas, and water differentiation and imaging visualisation. It also provides rapid, accurate detection of oil and water content in drilling mud and oil sludge, delivering professional solutions for users. Equipped with specialised modules for high-temperature high-pressure and low-temperature high-pressure conditions, the system can realistically simulate formation environments for online visualised displacement experiments (e.g., waterflooding, oilflooding), gas hydrate growth experiments, and unfrozen water studies in permafrost.
Core and Cuttings
1) One-dimensional Relaxation Spectrum Analysis (Conventional/Dense)
a) Porosity
b) Permeability
c) Bound Fluid Saturation
d) Mobile Fluid Saturation
e) Oil Saturation
f) Clay-bound Water Content
g) Pore Fluid Distribution
h) Pore Size Distribution
i) T1 and T2 Cut-off Times
2) Multi-dimensional NMR Oil-Water Diffusion Analysis
a) Oil and Gas Differentiation (T1-T2 Correlation)
b) Oil and Water Differentiation (D-T2 Correlation)
c) T2 Relaxation Time vs Internal Gradient (T2-G)
3) Core Imaging
Drilling Fluid Analysis
1) Measurement of Oil Content in Drilling Fluid
a) Oil Type Analysis (Heavy, Medium, Light Oil)
b) Oilfield Contamination (Rapid Detection of Oil and Water in Mud)
2) Crude Oil Property Evaluation
Geotechnical and Coal Mining
a) Porosity Measurement
b) Analysis of Freeze-Thaw Mechanisms in Soil and Rock
c) Rock Fracture Development under Freeze-Thaw Conditions
d) Study of Formation and Decomposition Conditions of Gas Hydrates
Simulation of Low-Temperature High-Pressure Environments for Freeze-Thaw Analysis
e) Experimental Analysis of Seepage Mechanisms
f) Dynamic, Real-Time Monitoring of Oil and Water Saturation and Distribution During Displacement Experiments
g) Imaging and Visualisation of the Displacement Process
Simulation of High-Temperature High-Pressure Conditions for Seepage Mechanism Analysis and Displacement Efficiency Evaluation
1. Conventional Core Porosity and Saturation Testing

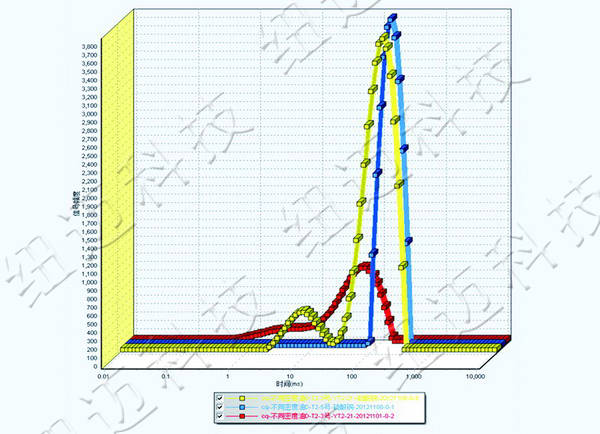
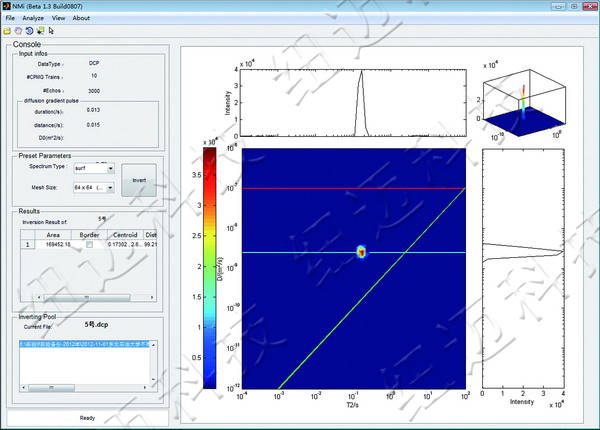
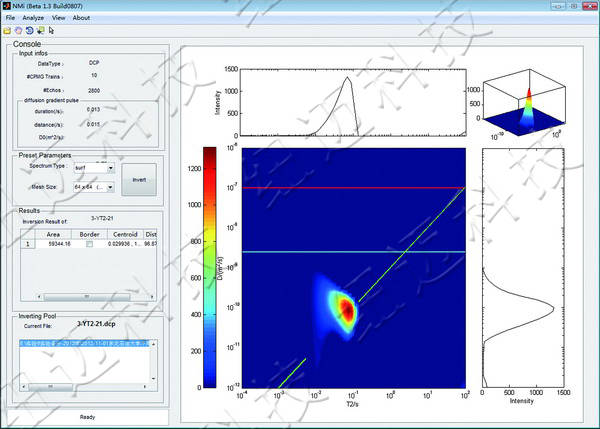
2. Multi-dimensional NMR Diffusion Analysis
2D Mixed Oil Experiment

3. Drilling Fluid Oil and Water Content Analysis
Measurement of Oil Content in Drilling Fluid
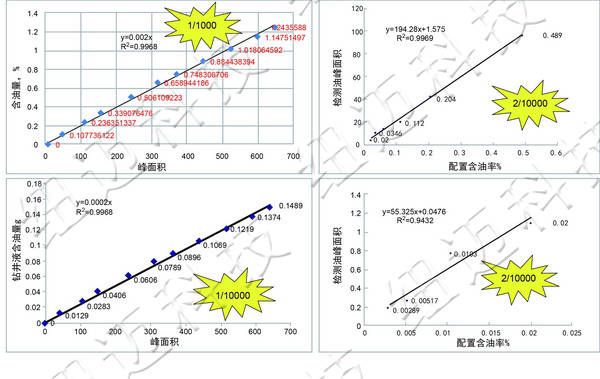

The NMR device can stably detect a minimum oil content of 0.01% and can measure as low as 0.002%.
Oil and Water Content Tests of Drilling Fluids from Various Well Depths
4. Visualised Observation of Permafrost Thawing
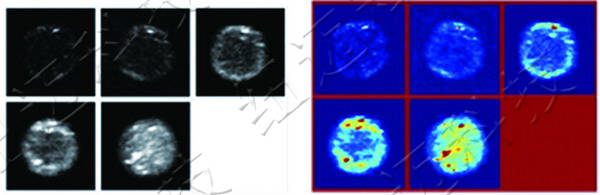
In the image above, bright signals represent water. As thawing progresses, the signals propagate from the exterior to the interior until fully melted.
High-Pressure Displacement
MnCl2 Solution Oil Displacement (Waterflooding) Process
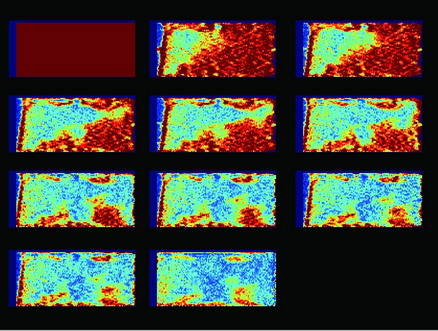
Core Properties
Porosity (Ø) | Length (mm) | Pore Volume (ml)
0.240 | 49.0 | 5.77
1. In the image, red represents oil signals, and green represents water signals.
2. The left image shows the waterflooding process from 0PV to 1PV, where 0PV represents fully oil-saturated core. The image illustrates water entering the core and displacing oil. As displacement progresses, a clear oil-water interface forms along with preferential flow channels.
Shale TE Relaxation Test Experiments
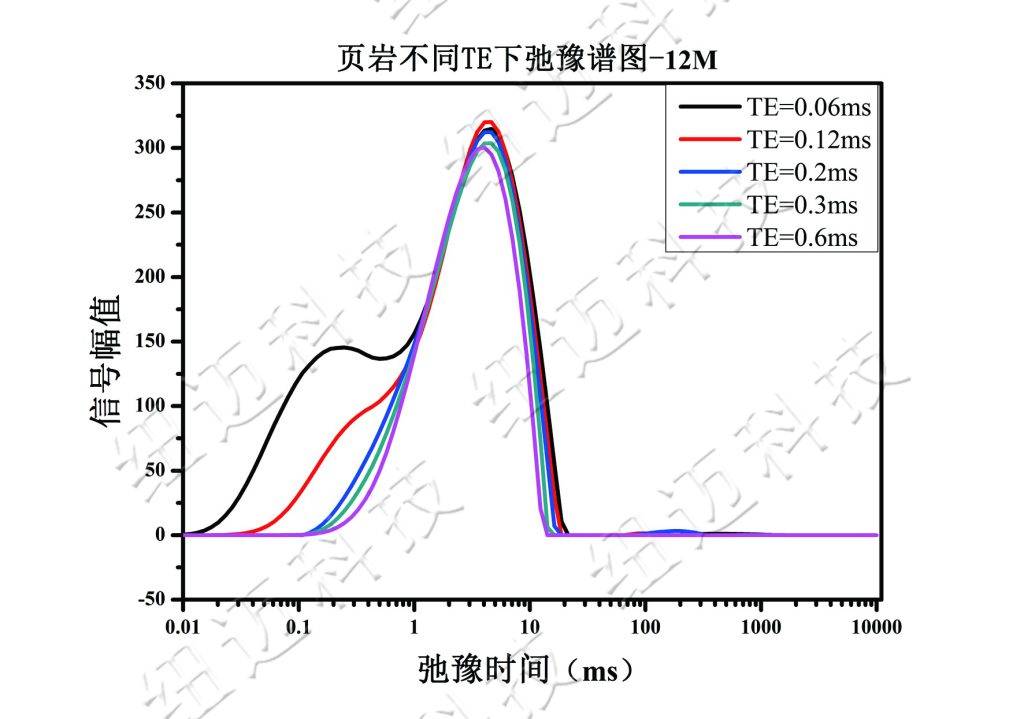
As shown, the short relaxation components in shale decrease as TE increases, indicating that higher TE values result in signal loss during shale measurement.
Phone: 400-060-3233
After-sales: 400-060-3233


Back to Top