Nuclear magnetic resonance instruments can be categorised by magnetic field strength:
3.0T ——— High-field NMR;
1.0T – 3.0T —— Mid-field NMR;
0.1T – 1.0T —— Low-field NMR;
< 0.1T ——— Ultra-low-field NMR;
Low-field NMR refers to instruments operating at relatively low magnetic field strengths. This technique is widely applicable and continues to evolve. Low-field NMR analyses and measures samples primarily based on four modes: (1) signal amplitude; (2) imaging (2D signal mapping); (3) relaxation time (T1, T2); and (4) diffusion coefficient measurements.
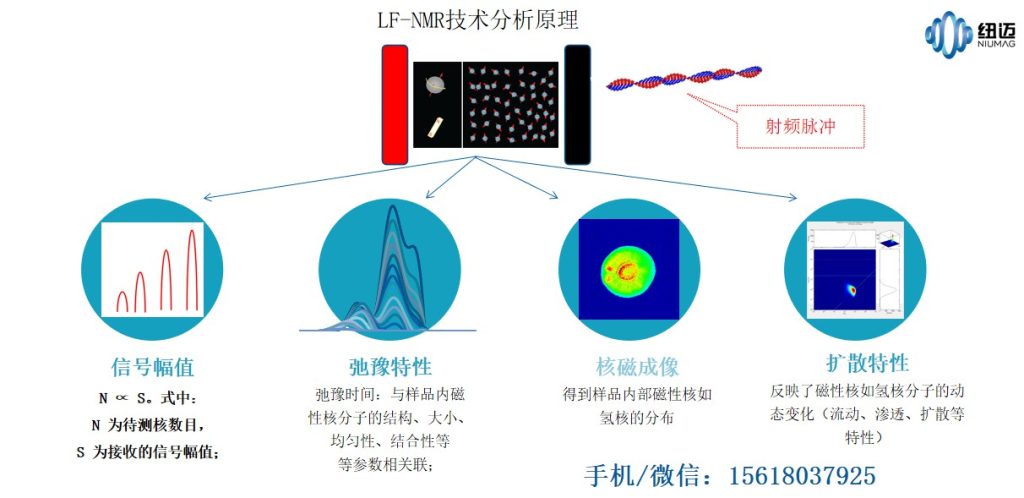
Low-field NMR is increasingly used across multiple industries including food & agriculture, geology, petrochemicals, biomedicine, and material sciences — becoming an essential tool for modern analytical testing.
Below is an image of a low-field NMR instrument operating at 0.5T:
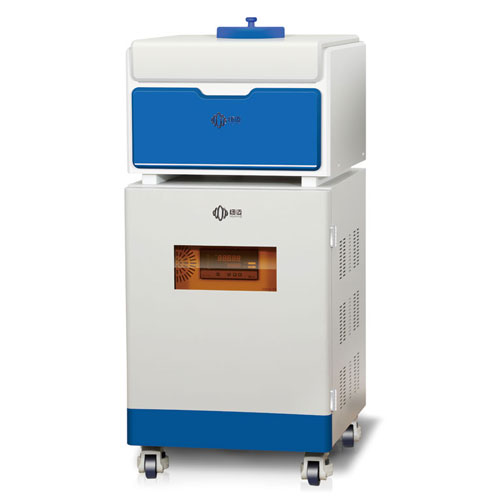

Low-Field NMR Imaging and Analysis Instrument
High-field NMR instruments are primarily used to test molecular chemical structures. By measuring chemical shifts, they provide insights into molecular internal structures and are mainly used for microscopic research (within molecules), capable of performing multi-nuclear spectra measurements such as 1H, 13C, 31P, 15N, etc.
Low-field NMR is mainly used to measure molecular dynamics between molecules, providing information on molecular motion and interactions via relaxation times. Its research domain is submicroscopic (between molecules), and it can measure properties like glass transition temperature, crosslink density in polymers, relaxivity of contrast agents, pore size distribution, porosity, and more. Low-field NMR is widely applied in the food, petroleum, pharmaceutical, textile, and polymer industries.
High-field NMR boasts high sensitivity, resolution, and signal-to-noise ratio. However, it requires a high degree of sample uniformity, deionized liquids, and powdered solids. The instruments are expensive, require special installation spaces, shielding facilities, and cooling with liquid nitrogen or helium. Maintenance costs are also high.
Low-field NMR uses permanent magnets, is compact, portable, easy to maintain, and can be integrated with other equipment or accessories, making it ideal for online high-throughput testing. The instruments are inexpensive, already shielded, and do not require special installation conditions. Low-field NMR is perfect for online process monitoring, industrial quality control, and product inspection.
Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance technology primarily detects hydrogen protons (H) and can also be used for fluorine (F) signal testing. After applying a specific frequency radiofrequency pulse, hydrogen-containing samples generate NMR signals. The NMR signals of hydrogen correspond to two main parameters: T1 and T2. By testing the relaxation times of T1 and T2 and modeling them, low-field NMR can be used in various research fields, including food, agriculture, petroleum exploration, polymers, solid fat content, and more. Various methods have already been established as international standards and industry-specific standards.
Due to its lower equipment costs and the relatively low barrier for research use, low-field NMR is widely applied and continues to expand. It offers many advantages, such as speed, high accuracy, the ability to obtain multiple parameters from a single measurement, no sample loss, simple sample preparation, and no impact on the health of operators or the environment. As a result, many applications that originally relied on other traditional testing methods are now exploring the use of nuclear magnetic resonance technology.
1). Application of Low-Field NMR in the Food Industry:
◆ Solid fat content testing for palm oil, butter, and other fats (SFC, Solid Fat Content)
◆ Oil and moisture content testing for oilseeds and seed residues
◆ Solid fat content in chocolate and related products
◆ Total fat content
◆ Droplet size analysis of water-in-oil and oil-in-water emulsions
◆ Oil, moisture, and protein content in dry and wet foods and feed
◆ Glass transition temperature of food
◆ Temperature-dependent food studies (heating modes, thermal denaturation, cooking process)
◆ Food storage process, moisture migration, and distribution studies
◆ Rapid moisture content testing of biscuits
◆ Oil content testing of dry snacks
◆ Gel hydration studies
◆ Quality changes during drying and rehydration processes
2). Application of Low-Field NMR in Agriculture:
◆ Seed oil and moisture content testing
◆ Seed germination process studies
◆ Automated breeding of oilseeds (sorting by oil content)
◆ Plant root imaging research
◆ Agricultural product drying studies
3). Application of Low-Field NMR in the Textile Industry:
◆ Oil content in fibers
◆ Polymer coating content
◆ Fluorine coating measurement on fibers and textiles
4). Application of Low-Field NMR in the Materials Industry:
◆ Xylene solubles content in polypropylene
◆ Density and crystallinity of polyethylene
◆ Rubber content in acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene and polystyrene
◆ Crosslink density in elastomers
◆ Oil content in sulfur powder samples
◆ Rubber content in polystyrene
◆ Filler content in asphalt shingles
◆ Calcium fluoride content in fluorspar
◆ Plasticizer content in PVC
◆ Polyethylene density measurement
◆ Polymer molecular weight testing
◆ Zeolite moisture content testing
◆ Oil content in ammonium explosives
◆ Oil content testing in wastewater
◆ Fluoride content measurement in fluorinated alumina
◆ Crosslink density in rubber
◆ Polymer aging and curing process dynamic evaluation
◆ Temperature-dependent polymer performance studies
◆ Polymer modification evaluation
◆ Soft-hard segment analysis in polymers
◆ Material hydrophilicity and water absorption process studies
◆ Pore size and distribution studies in membrane materials
◆ Water migration analysis in membrane materials
◆ Gel material hydration evaluation
◆ Pore size and distribution studies in wood
◆ Fluoride content in toothpaste
◆ Melting properties of cosmetics
5). Application of Low-Field NMR in the Petrochemical Industry:
◆ Hydrogen content in hydrocarbons
◆ Oil content in wax/paraffin
6). Application of Low-Field NMR in the Pharmaceutical Industry
◆ Fat and muscle content in live mice and rats
◆ Non-contact weighing
◆ Moisture and solvent content in powders and tablets
◆ Relaxation time, relaxivity, in vitro imaging, and in vivo MRI of contrast agents
◆ In vivo MRI of rats and mice, multimodal imaging
7). Application of Low-Field NMR in Suspended Systems:
◆ Relaxation of microemulsions
◆ Adsorption behavior in mixed polymer systems
◆ Competitive adsorption of polymers on silica
◆ Barium titanate precipitation process
◆ Accelerated aging effects of gold and silver nanoparticles
◆ Surface area of suspended particulate systems
◆ Impact of grinding on the surface area of suspensions
◆ Surface area of silicon carbide suspensions
◆ Relaxation behavior of mixed particle suspensions
◆ Relaxation behavior during the grinding process of pharmaceutical raw materials
◆ Droplet size measurement
◆ Powder quality control and dispersion process research
8). Application of Low-Field NMR in Geotechnical Energy Fields:
◆ Porosity, pore size distribution, permeability, saturation testing
◆ Mechanical damage patterns and mechanisms
◆ Soil moisture state, moisture migration, frozen soil unfrozen water content analysis
◆ Overall moisture content and moisture distribution studies in sludge
◆ Sludge purification treatment process research
◆ Water absorption, permeability, water retention, and waterproofing testing in building materials
◆ Cement curing process research
9). Application of Low-Field NMR in Porous Materials:
◆ Pore size distribution studies
◆ Pore size studies
◆ Low-temperature nanopore testing
Low-field NMR instruments consist of six main components: industrial computer, spectrometer system, radiofrequency unit, gradient unit, magnet cabinet, and temperature control unit. According to the tasks, the system is composed of five main components: industrial computer, radiofrequency system, gradient system, magnet, and temperature system. The industrial computer receives operator commands, generating control signals through software that coordinates the spectrometer system components. It also handles data processing, storage, image reconstruction, and display tasks. The radiofrequency system is responsible for transmitting radiofrequency pulses and receiving sampled signals. The gradient system generates gradient magnetic fields, and the magnet provides a uniform, stable primary magnetic field. The temperature system manages temperature control in the magnet cabinet.

Low-Field NMR Instrument Architecture Diagram
Low-Field NMR Imaging Software:
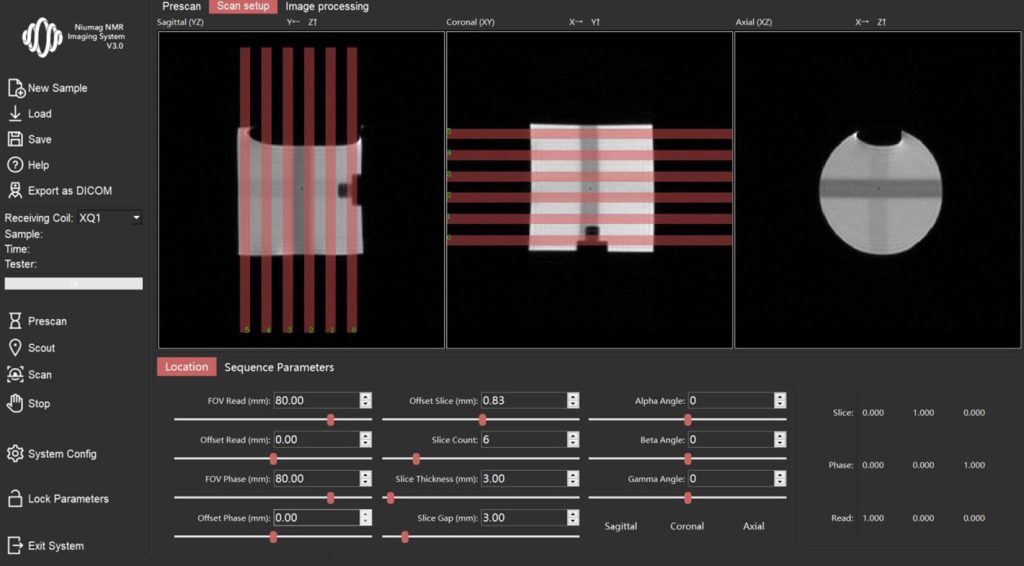
Low-Field NMR Analyzer Software:

Time-domain NMR Analyzer Software Interface
Phone: 400-060-3233
After-sales: 400-060-3233


Back to Top