Drying refers to the process of removing moisture from food, thereby reducing its water activity. This inhibits microbial growth, enzymatic activity, and chemical reactions—achieving the goal of long-term preservation.
1. Extended shelf life – Dried foods have reduced water activity, making them suitable for long-term storage at room temperature.
2. Improved processability – For example, proper drying of soybeans or peanuts improves dehulling efficiency and enhances downstream processing and product quality.
3. Facilitated transportation and distribution – Dried foods weigh less and take up less space, reducing packaging, storage, and logistics costs. They are easier to transport and store.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are powerful tools for analyzing water activity and behavior in food systems. These water molecules carry key structural and environmental information, and provide insights into internal changes during processing and storage.
Thanks to its non-destructive testing nature, NMR offers a clear advantage for food science applications. Today, it has been successfully applied in drying and storage research for a wide variety of food materials.
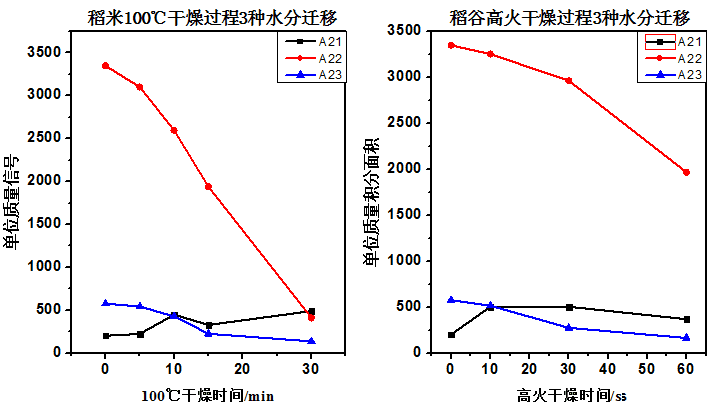
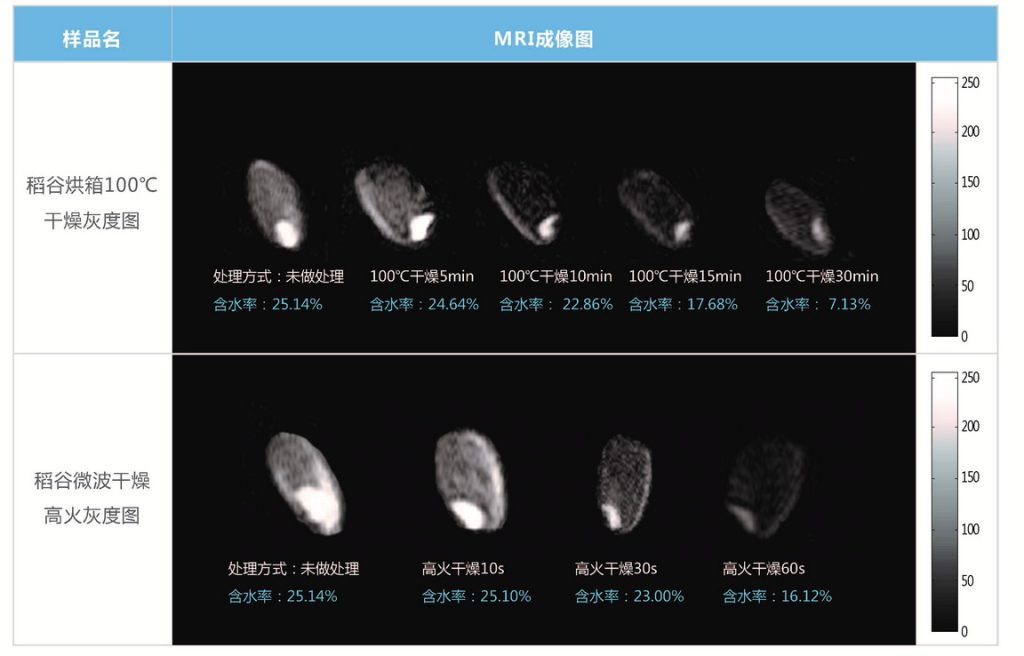

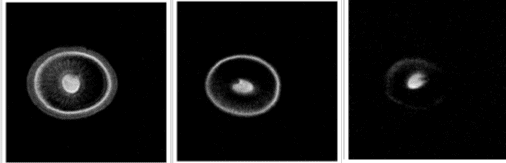
MRI scans of mushrooms under varying drying durations
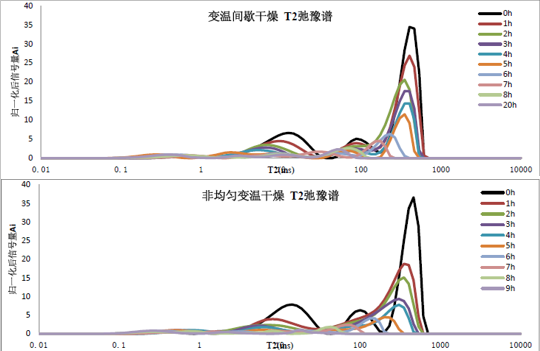
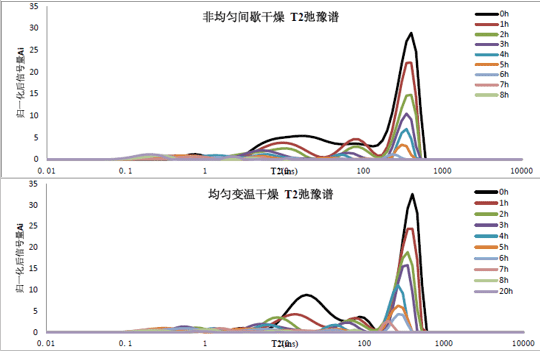
T2 distribution profiles of mushrooms under different drying methods
Follow us on WeChat: niumag2003
Niumag Technologies is dedicated to the R&D, manufacturing, and application services of NMR imaging and analytical instruments—providing you with comprehensive application solutions for food drying, quality control, and research.
Phone: 400-060-3233
After-sales: 400-060-3233


Back to Top