The oiling agents applied to fibers are typically used as lubricants or antistatic agents. However, they can also serve as carriers for other chemical agents such as antimicrobials, flame retardants, and colorants. Oil content is an important quality control parameter—it directly determines whether the fiber meets performance requirements. Uneven oil distribution is a common issue in synthetic fiber production. Fibers with too little oil tend to generate static electricity, while overly oiled fibers are prone to sticking and entanglement. Both conditions negatively impact textile processing. Therefore, accurate measurement of fiber oil content is crucial for precise oiling control and production stability.

According to the current standard GB/T 6504-2008 “Test Methods for Oil Content in Chemical Fibers,” the approved methods include the extraction method (commonly referred to as the standard extraction method), neutral soap solution washing, refractive index method, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) method. In addition, petrochemical enterprises have developed several new methods for production efficiency, such as rapid extraction, atomic absorption, conductivity, distilled water oscillation, and UV spectroscopy—each tailored for specific product types.
1. Standard Extraction Method: This method uses specific organic solvents to dissolve the oiling agents in the fiber sample. The oil is extracted using a fat extractor, the solvent is evaporated, and the remaining oil is weighed. The oil content is calculated based on the weight of the sample and extracted oil.
2. Neutral Soap Solution Washing: This method relies on the affinity between soap solution and oiling agents. The washing process transfers oil from the fiber into the soap solution. The oil content is determined by comparing the sample weight before and after washing.
3. Refractive Index Method: This method measures the refractive index of an unknown substance by determining the critical angle of total reflection. It is then used to quantify specific components in a solution and assess the purity of the material.
4. Low-Field NMR Method: This technique involves applying a pulsed magnetic field to the fiber sample. Once the field is removed, the resulting magnetic signal is detected. Since the signal from the fiber decays faster than that from the oil, their difference can be used to calculate the oil content of the sample.
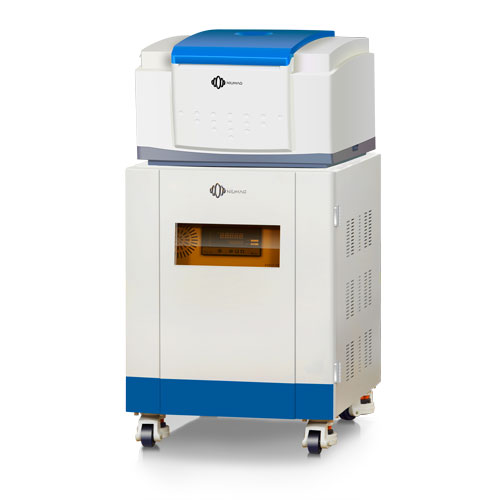

Traditional oil content testing methods—mainly extraction—have several limitations, including long test times, delayed results, use of harmful solvents, labor-intensive procedures, and potential for operator error. To overcome these challenges, Niumag developed an LF-NMR-based method specifically for measuring fiber oil content.
Key Advantages: Fast, Accurate, Non-Destructive
Only 30 seconds required per test—quick response for high-throughput sample processing. Ideal for real-time, on-line quality control.
Recognized in national standards—NMR ensures precise, repeatable, and environmentally friendly measurements. Non-destructive testing allows for longitudinal experiments on the same sample.
Phone: 400-060-3233
After-sales: 400-060-3233


Back to Top