Time-domain NMR(nuclear magnetic resonance) is a powerful technique that has found widespread applications in various fields, including food science. One of its key applications is the measurement of fat content in foods, particularly in chocolates. The accuracy and reproducibility of NMR-based measurements make it a reliable tool for quality control and product development in the chocolate industry.

The theory behind time-domain NMR lies in the interaction of nuclear spins with magnetic fields. In this technique, a sample is placed in a strong static magnetic field, which aligns the nuclear spins of atoms within the sample. A pulse of radiofrequency radiation is then applied, causing the spins to flip and emit a characteristic radiofrequency signal as they return to their equilibrium state. The decay of this signal, known as the free induction decay (FID), is analyzed to extract information about the sample’s composition.
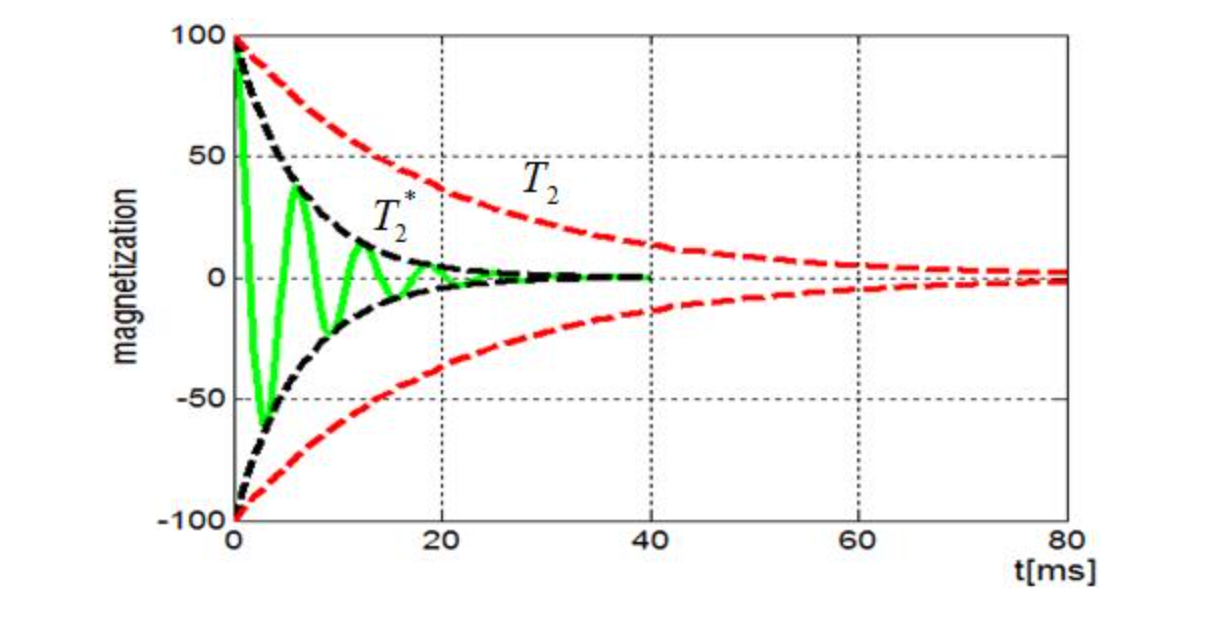
In the context of chocolate fat content measurement, NMR is particularly useful because fats have a distinct signature in the FID signal. The technique allows for the quantitative determination of fat content by measuring the intensity and decay rate of the FID signal from the fat protons. This can be achieved by comparing the signal from the chocolate sample to a reference or calibration curve established using samples with known fat concentrations.

The application of time-domain NMR in chocolate fat content measurement offers several advantages. Firstly, it is a non-destructive technique, meaning that the sample remains intact after measurement, allowing for further analysis or use. Secondly, NMR provides rapid and accurate results, enabling real-time quality control during production. Additionally, the technique is highly sensitive and can detect even small changes in fat content, making it suitable for precision measurements.
In summary, time-domain NMR is a powerful tool for measuring chocolate fat content. Its theoretical foundation lies in the interaction of nuclear spins with magnetic fields, and its application in food science allows for accurate and rapid determination of fat content in chocolates. The technique offers numerous advantages, including non-destructiveness, rapidity, accuracy, and sensitivity, making it an invaluable tool for the chocolate industry.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG