Background of Low Field NMR Study on Rubber Crosslinking
The degree of cross-link, also known as the cross-linking density, is usually expressed in terms of cross-link density or the number-average molecular weight between two adjacent cross-link points or the number of moles of cross-link points per cubic centimeter. The rubber with a small degree of cross-linking has better elasticity, while the rubber with a large degree of cross-linking has poor elasticity. If the degree of cross-linking increases, the mechanical strength and hardness will increase, and eventually the elasticity will be lost.
The degree of rubber crosslinking has always been a problem in the industry. The traditional swelling method has low test accuracy and is subject to large human subjective factors. In the NMR method, the polymer relaxation decay curve changes with the change of the state of the internal components of the sample, and the cross-linked and non-cross-linked chain signals can be quickly and non-destructively obtained by NMR relaxation technology to obtain the degree of cross-linking.
The solvent part in the polymer has strong fluidity and slow decay; the non-cross-linked segment has certain molecular motion characteristics, and the decay is relatively slow; while the cross-linked segment is bound to a large degree, the molecular motion characteristics are small, and the decay is faster. Compared with the traditional SE or CPMG sequence acquisition, when using the new MSE-CPMG sequence acquisition, the NMR signal is reversed back and forth within the dead time range by applying combined pulses, so as to maintain the original NMR signal intensity as much as possible. The shorter relaxation information is collected, and the test accuracy of the crosslinking density is further improved.
Principle of Low Field NMR Study on Rubber Crosslinking
Low-field NMR analysis technology uses pulses to excite hydrogen protons in material samples to resonate, and after the pulse is stopped, hydrogen protons relax. The relaxation times of hydrogen protons in different states in the sample are different. The detection and analysis of the relaxation signal can directly or indirectly detect some properties of the material. The low-field NMR method uses low-field nuclear magnetic resonance analysis technology to evaluate the movement of H molecules on the hydrocarbon chain and analyze the cross-linking degree of the sample according to the relaxation analysis model. The test process does not require chemicals, is non-destructive to the sample, and the test speed is fast. Generally, the test can be completed within 3 minutes.
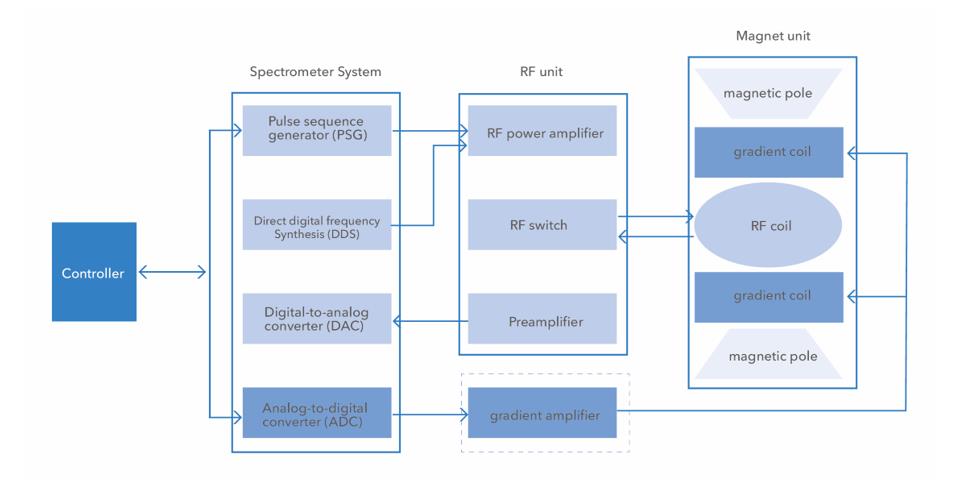
The composition of the low-field NMR analyzer
- The NMR crosslinking density meter usually consists of the following parts,
- Control unit (control core, interface for human-computer interaction),
- Magnet unit (the part that generates the radio frequency excitation and collects the signal),
In addition to the above parts, there are temperature control, power module, etc.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG