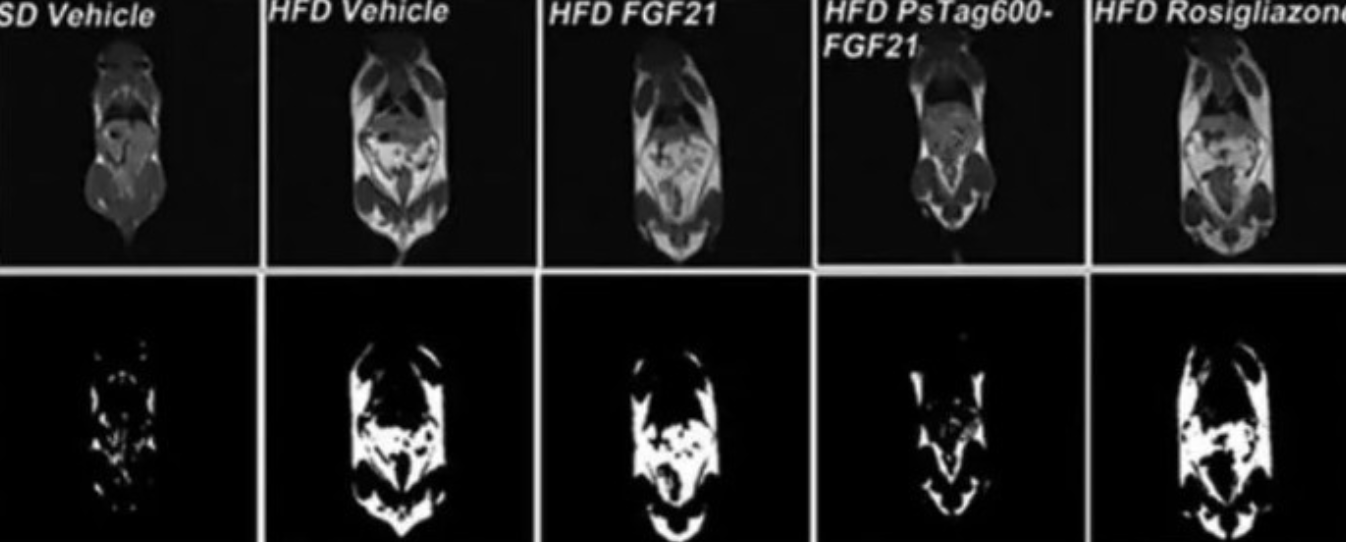
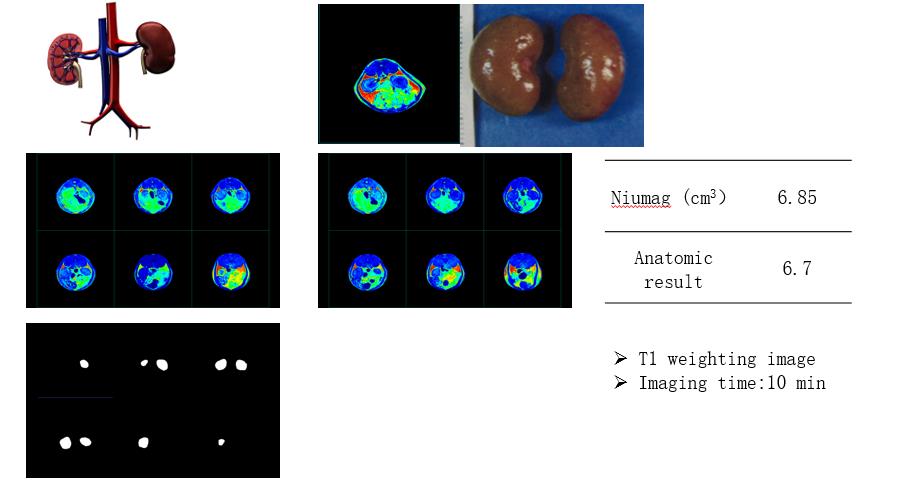
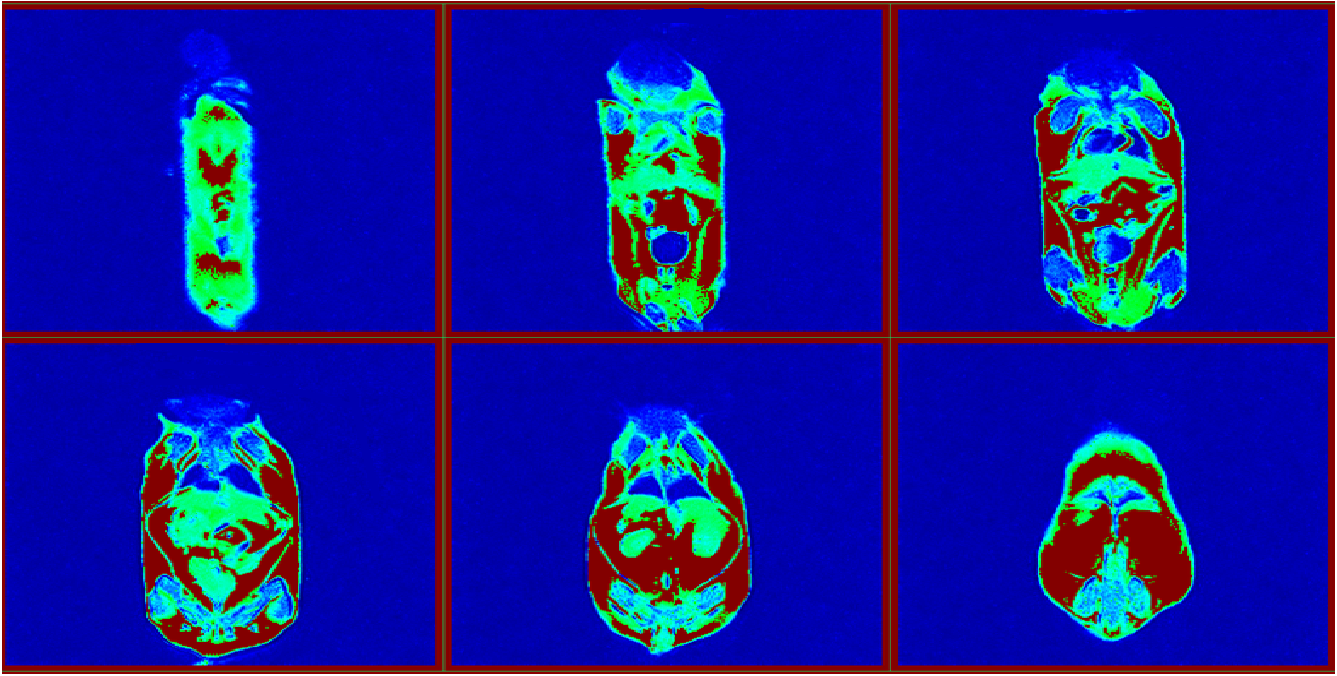
resonancia magnética del ratón by LF NMR
resonancia magnética del ratón (Imagen de resonancia magnética) is a groundbreaking medical imaging technique that plays a pivotal role in research involving mice. By utilizing a powerful magnetic field, ondas de radio, and advanced computing, resonancia magnética del ratón produces intricate and comprehensive images of a mouse’s internal structures. This non-invasive method allows researchers to delve into the intricacies of organs, tejidos, and other vital components within a living mouse.
resonancia magnética del ratón Appllication
The applications of resonancia magnética del ratón are wide-ranging and immensely valuable. It enables the imaging of various structures, such as the brain, corazón, pulmones, hígado, riñones, and numerous other organs. Además, resonancia magnética del ratón proves indispensable in investigating disease processes, monitoring the effects of treatments, and evaluating drug efficacy.
Different imaging techniques can be employed for resonancia magnética del ratón, each serving specific research purposes. T1-weighted imaging, Imágenes potenciadas en T2, imágenes ponderadas por difusión, and functional MRI are among the techniques that researchers may utilize based on the nature of their study.
resonancia magnética del ratón is especially significant for researchers investigating diseases and conditions that impact mice, como el cáncer, enfermedad de alzheimer, Enfermedad de Parkinson, and cardiovascular ailments. Además, it provides an avenue to study the effects of environmental toxins, drogas, y otros tratamientos en el cuerpo del ratón..
resonancia magnética del ratón and other Imaging Methods
There are several methods available to obtain images of mice for research purposes. Tomografía microcomputada (micro-CT) utilizes X-rays to create high-resolution 3D images, primarily beneficial for studying bone structure, but capable of visualizing other tissues and organs as well. Optical imaging, utilizing light, allows researchers to study various biological processes, including gene expression and blood flow, through methods like bioluminescence imaging (CONVERTIRSE) e imágenes de fluorescencia (FLI). Ultrasonido, employing sound waves, is particularly useful for cardiovascular studies and examining blood flow. Tomografía de emisión de positrones (MASCOTA) involves injecting a radioactive tracer into the mouse body and then detecting positrons emitted by the tracer using a PET scanner, which helps study metabolism and receptor binding. Similarmente, Tomografía computarizada por emisión de fotón único (ESPECTACULAR) also employs radioactive tracers but uses a different type of tracer for studying a range of biological processes.
These methods, whether used individually or in combination, offer a comprehensive understanding of mouse anatomy, biología, and disease processes. They serve as invaluable tools for enhancing our knowledge of medical research and advancing treatments.
resonancia magnética del ratón por RMN de campo bajo
One promising technology for resonancia magnética del ratón is Low Field NMR (Resonancia magnética nuclear). Operating at a lower magnetic field strength than traditional clinical MRI machines, Low Field NMR holds significant potential in preclinical research involving mice.
The appeal of Low Field NMR lies in its affordability and accessibility, as it does not necessitate a specialized facility for operation. Además, it allows researchers to study a diverse array of mouse models and tissues, incluyendo el cerebro, hígado, riñones, and other vital organs.
The key advantage of Low Field NMR is its ability to study samples in their natural state, eliminating the need for invasive procedures. This is crucial for comprehending the natural structure and function of mouse tissues and organs, advancing our understanding of disease processes, and fostering the development of novel treatments.
La RMN de campo bajo aporta varias ventajas sobre las máquinas tradicionales de resonancia magnética de campo alto. Su menor costo y su reducida sensibilidad a los artefactos causados por el movimiento o los implantes metálicos mejoran la calidad de la imagen y la convierten en una opción atractiva para investigadores con limitaciones presupuestarias.. Además, its decreased occurrence of motion artifacts is especially beneficial for studying organs like the mouse heart, which are prone to movement during imaging.
En conclusión, resonancia magnética del ratón, with its revolutionary techniques and evolving technologies like Low Field NMR, continues to shape the landscape of preclinical research and medical advancements.
 mohoso
mohoso